Blog
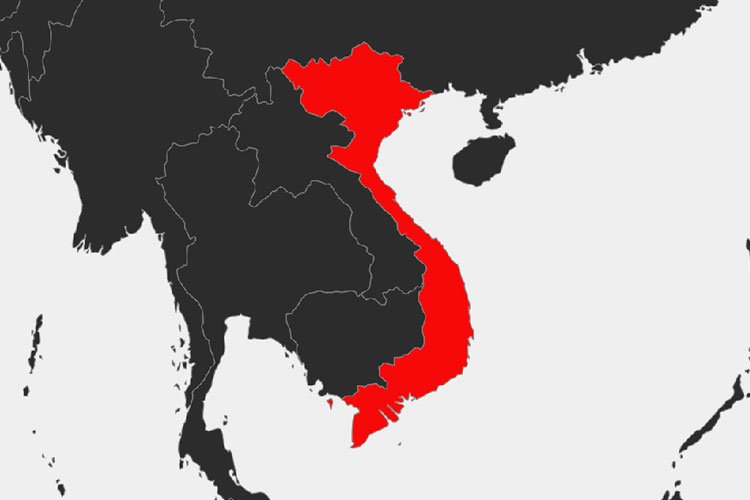
Where is Vietnam on the map?
Introduction
Vietnam, a Southeast Asian gem, is renowned for its lush landscapes, vibrant culture, and historical significance. Nestled along the eastern edge of the Indochinese Peninsula, Vietnam offers a unique blend of natural beauty, ancient traditions, and modern development. In this article, we will explore Vietnam’s geographical location, its historical context, and its rich cultural heritage, providing a comprehensive understanding of this captivating country.
Geographic Location of Vietnam
Vietnam is situated in Southeast Asia, bordered by China to the north, Laos and Cambodia to the west, and the South China Sea to the east and south. The country extends from approximately 8° to 24° north latitude and from 102° to 110° east longitude. This strategic position has historically made Vietnam a crucial point for trade, cultural exchange, and strategic military significance.
[mapsvg id=”12″]
Major Cities and Regions
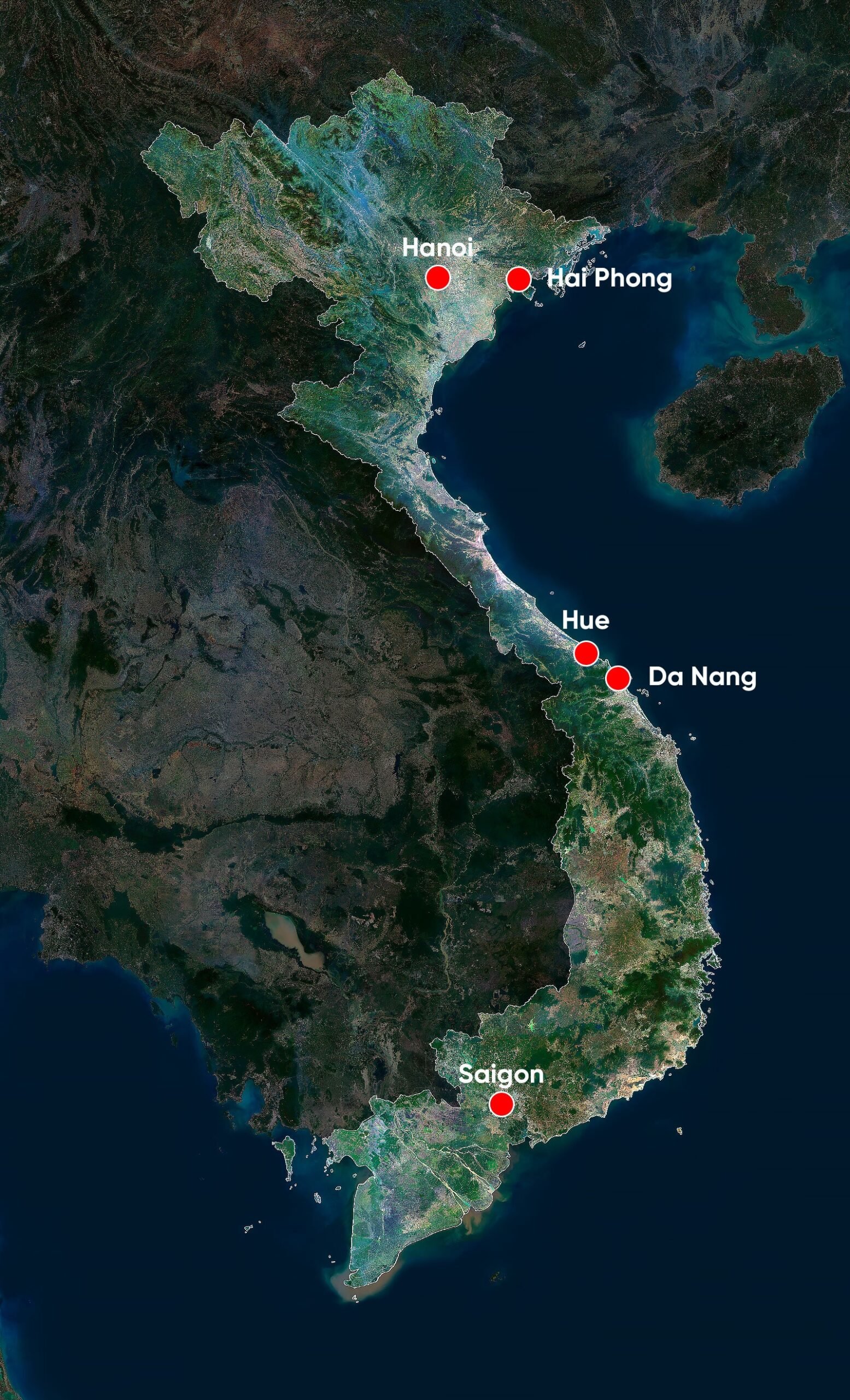
Vietnam is divided into several distinct regions, each offering unique geographical and cultural attributes. The major cities include:
- Hanoi: The capital city, located in the northern part of the country, is known for its centuries-old architecture, rich history, and vibrant street life. Hanoi is also the political and cultural heart of Vietnam.
- Ho Chi Minh City (Saigon): Situated in the south, Ho Chi Minh City is Vietnam’s largest city and its economic powerhouse. The city is famous for its bustling markets, French colonial landmarks, and dynamic urban atmosphere.
- Da Nang: Located in central Vietnam, Da Nang is known for its sandy beaches, modern skyline, and proximity to ancient cultural sites such as Hoi An and My Son.
- Hue: Also in central Vietnam, Hue is renowned for its historical significance as the former imperial capital. The city boasts numerous temples, pagodas, and the UNESCO-listed Imperial City.
- Hai Phong: A major port city in the north, Hai Phong is an important industrial center and gateway to Ha Long Bay, another UNESCO World Heritage site.
Unique Geographical Features
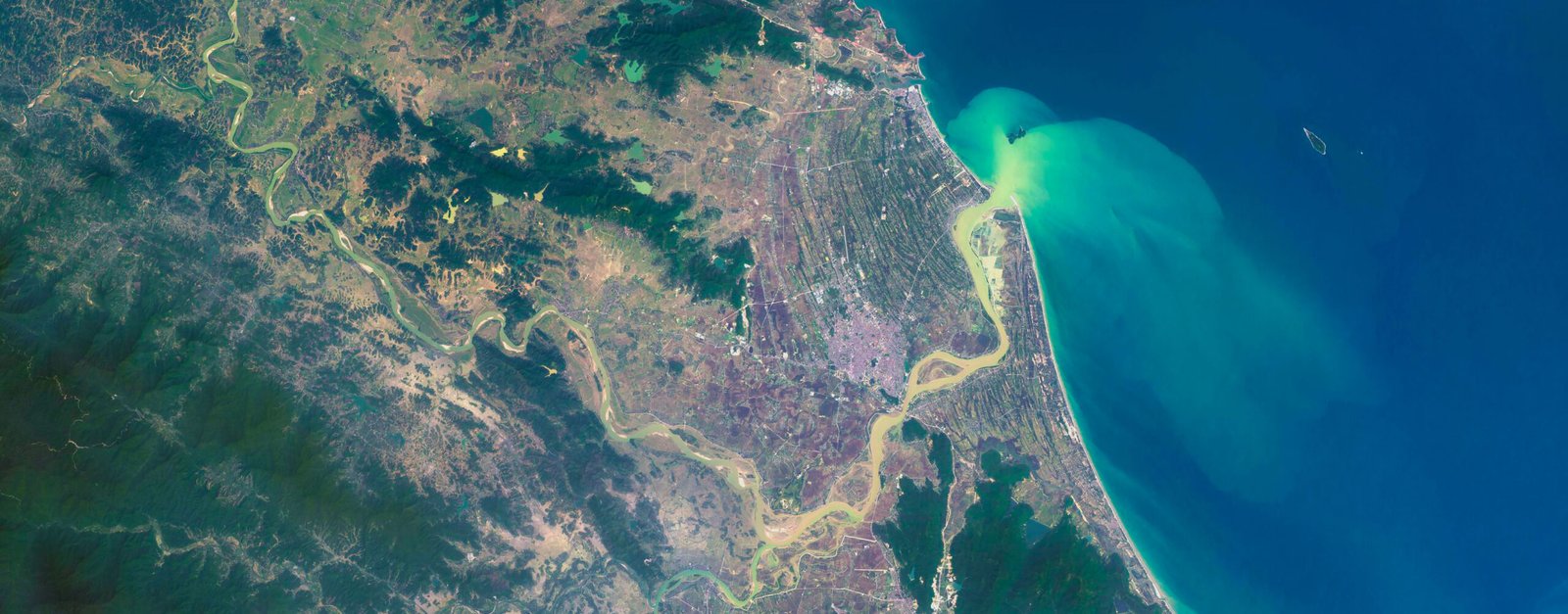
Vietnam’s diverse landscape includes everything from rugged mountains and dense forests to fertile river deltas and pristine beaches. Some of the country’s most notable geographical features are:
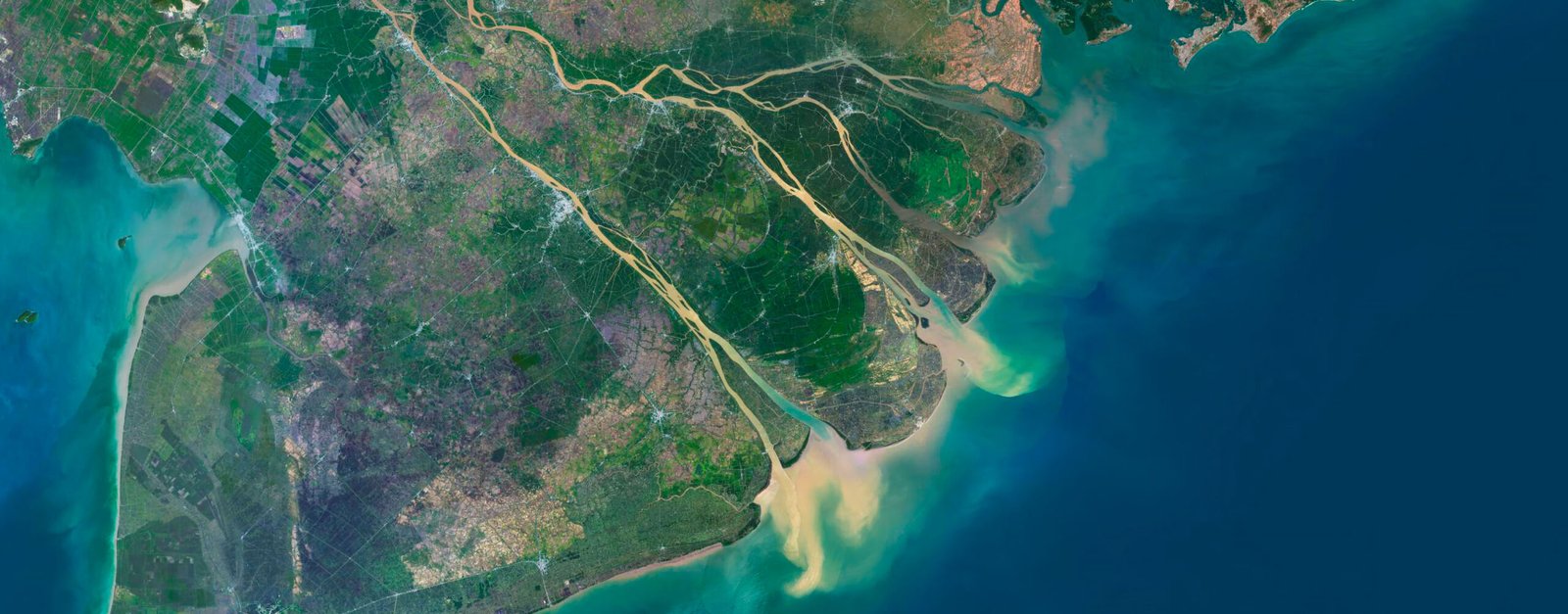
- The Red River Delta: Located in the north, this fertile region is the cradle of Vietnamese civilization and an essential area for agriculture and industry.
- The Annamite Range: Stretching along the western border, these mountains provide stunning landscapes and are home to many ethnic minority communities.
- The Mekong Delta: In the south, this vast network of rivers and canals is a vital agricultural area known for its rice paddies and floating markets.
- Ha Long Bay: Famous for its emerald waters and thousands of limestone islands, Ha Long Bay is one of Vietnam’s top tourist destinations and a UNESCO World Heritage site.
- Phu Quoc Island: Located off the southwestern coast, this tropical paradise is known for its white-sand beaches, clear waters, and luxury resorts.
Historical Context
Vietnam’s history is marked by periods of foreign domination, fierce independence struggles, and significant cultural achievements. Understanding its historical context provides valuable insights into the country’s identity and resilience.
Ancient Kingdoms
Vietnam’s recorded history dates back over 2,000 years, with the establishment of early kingdoms such as Van Lang and Au Lac. These early states laid the foundation for the development of Vietnamese culture and society.
Chinese Domination and Independence
For over a thousand years, Vietnam was under Chinese rule, which greatly influenced its culture, language, and administrative systems. However, the Vietnamese people maintained a strong sense of identity and frequently rebelled against their foreign rulers. In 938 AD, under the leadership of Ngo Quyen, Vietnam achieved independence and established its own dynastic rule.
Colonial Era and Modern History
In the 19th century, Vietnam fell under French colonial rule, which lasted until the mid-20th century. The struggle for independence, led by figures such as Ho Chi Minh, culminated in the establishment of the Democratic Republic of Vietnam in 1945. The country was later divided into North and South Vietnam, leading to the Vietnam War. In 1975, the country was reunified as the Socialist Republic of Vietnam.
Cultural Significance
Vietnam’s rich cultural heritage is reflected in its traditions, festivals, and daily life. The country’s culture is a harmonious blend of indigenous practices and external influences from China, India, France, and the United States.
Traditional Practices
Vietnamese culture places a strong emphasis on family, community, and respect for elders. Traditional practices such as ancestor worship and communal activities play a significant role in daily life. Festivals such as Tet (Lunar New Year) and the Mid-Autumn Festival are celebrated with great enthusiasm and are marked by vibrant parades, traditional music, and dance.
Culinary Delights
Vietnamese cuisine is renowned for its balance of flavors, fresh ingredients, and diverse regional specialties. Iconic dishes include pho (noodle soup), banh mi (Vietnamese sandwich), and spring rolls. Street food is an integral part of Vietnamese culinary culture, offering a wide array of delicious and affordable options.
Art and Architecture
Vietnamese art and architecture reflect the country’s historical and cultural evolution. Traditional art forms such as water puppetry, silk painting, and lacquerware are highly regarded. Architecturally, Vietnam boasts ancient temples, French colonial buildings, and modern skyscrapers, showcasing its rich heritage and contemporary dynamism.
Maps and Visual Representations
To gain a better understanding of Vietnam’s location and geography, high-resolution maps and 3D models are invaluable. These resources provide detailed views of the country’s topography and significant landmarks.
Conclusion
Vietnam, with its diverse landscapes, rich history, and vibrant culture, is a country that stands out on the map. Understanding its location and the unique features of its landscape and culture provides a deeper appreciation for this remarkable nation. Whether exploring its ancient cities, natural wonders, or cultural heritage, Vietnam offers a wealth of experiences for all who visit.