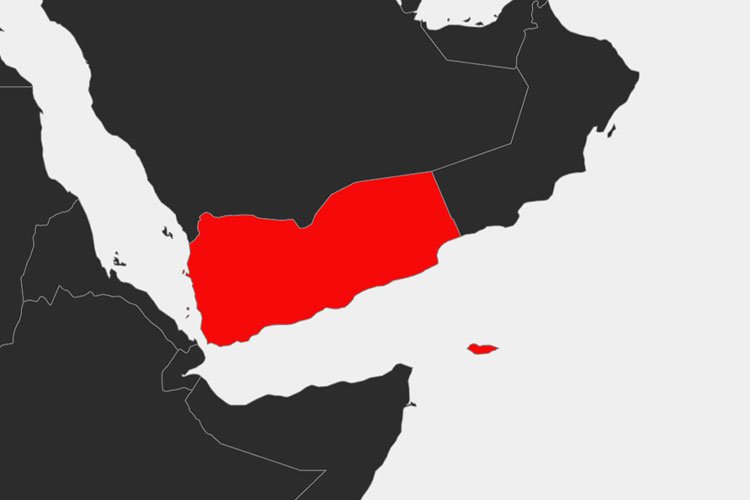
Where is Yemen on the map?
Introduction
Yemen, a country rich in history and cultural heritage, is often referred to as the cradle of ancient civilizations in the Arabian Peninsula. Its strategic location has made it a crossroads of cultures, commerce, and conquest for millennia. In this article, we will explore Yemen’s geographical position, its historical significance, and the unique cultural attributes that make it a fascinating destination.
Geographic Location of Yemen
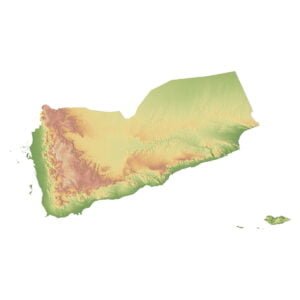
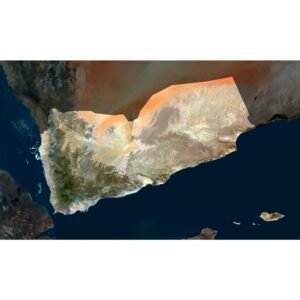
Yemen is situated in the southwestern corner of the Arabian Peninsula, bordered by Saudi Arabia to the north, Oman to the east, the Arabian Sea to the south, and the Red Sea to the west. Its coordinates range from approximately 12° to 19° north latitude and 42° to 55° east longitude. This strategic location has historically positioned Yemen as a vital link between Africa, the Middle East, and South Asia.
Major Cities and Regions
Yemen is divided into several distinct regions, each with its own unique geographical and cultural features. The major cities include:
- Sana’a: The capital city, known for its ancient architecture and historical significance. Sana’a is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world.
- Aden: A port city located on the southern coast, Aden has been a significant maritime center for centuries, with a natural harbor that has attracted traders and seafarers.
- Taiz: Situated in the highlands, Taiz is known for its vibrant cultural scene and historical sites, including the ancient Citadel of Cairo.
- Al Hudaydah: A crucial port city on the Red Sea coast, Al Hudaydah plays a vital role in Yemen’s economy and maritime activities.
- Mukalla: Located on the southeastern coast, Mukalla is known for its beautiful beaches and as a gateway to the Hadhramaut region.

Unique Geographical Features
Yemen’s diverse landscape includes mountain ranges, coastal plains, and arid deserts. Some of its most notable geographical features are:
- The Yemeni Highlands: This mountainous region runs parallel to the Red Sea coast and includes the country’s highest peak, Jabal an Nabi Shu’ayb, which stands at 3,666 meters (12,028 feet).
- The Tihama Plain: A narrow coastal plain along the Red Sea, known for its hot and humid climate.
- The Empty Quarter (Rub’ al Khali): Part of the vast desert that extends into Saudi Arabia, the Empty Quarter is one of the largest sand deserts in the world.
- Socotra Island: An isolated island in the Arabian Sea, Socotra is famous for its unique biodiversity and endemic species of flora and fauna.
Historical Context
Yemen has a rich history that dates back thousands of years, with evidence of ancient civilizations that thrived in the region. It was an important center for trade and commerce, connecting the Mediterranean, India, and Africa.
Ancient Kingdoms
Yemen was home to several powerful ancient kingdoms, including the Sabaean, Himyarite, and Hadhramaut kingdoms. The Sabaeans, known for the legendary Queen of Sheba, were famous for their impressive irrigation systems and trade in frankincense and myrrh.
Islamic Era
With the advent of Islam in the 7th century, Yemen became an important center of Islamic culture and learning. The region played a significant role in the spread of Islam throughout the Arabian Peninsula and beyond.
Modern History
In the 20th century, Yemen experienced significant political and social changes, leading to the unification of North Yemen and South Yemen in 1990. Despite ongoing challenges, Yemen continues to be a country of great cultural and historical importance.
Cultural Significance
Yemen’s cultural heritage is as diverse and rich as its history. The country is known for its distinctive architecture, traditional crafts, and vibrant cultural practices.
Architecture
Yemen is famous for its unique architectural styles, particularly the tower houses of Sana’a, which are built from mud bricks and decorated with intricate geometric patterns. The old city of Sana’a is a UNESCO World Heritage site, recognized for its historical and cultural significance.
Traditional Crafts
Yemen has a rich tradition of handicrafts, including silver jewelry, woven textiles, and pottery. These crafts are often produced using techniques that have been passed down through generations.
Cuisine
Yemeni cuisine reflects the country’s diverse cultural influences, with dishes that incorporate a variety of spices and ingredients. Popular dishes include salta (a meat stew with fenugreek), bint al-sahn (a honey cake), and malooga (a type of flatbread).
Maps and Visual Representations
To gain a better understanding of Yemen’s location and geography, high-resolution maps and 3D models are invaluable. These resources provide detailed views of the country’s topography and significant landmarks.
Conclusion
Yemen, with its rich history, diverse geography, and vibrant culture, is a country that stands out on the map. Understanding its location and the unique features of its landscape and culture provides a deeper appreciation for this fascinating nation. Whether exploring its ancient cities, natural wonders, or cultural heritage, Yemen offers a wealth of experiences for all who visit.
 Solar System
Solar System World
World Continents
Continents Peninsulas
Peninsulas Islands
Islands Countries
Countries States of America
States of America Canadian Provinces
Canadian Provinces Parks & Canyons
Parks & Canyons Fantasy
Fantasy Other
Other Planets
Planets Satellites
Satellites